Question 1
Polysorbate 80 is commonly used in eye drop formulations. What is its primary function in these formulations?
A) Preservative
B) Emulsifier
C) Lubricant
D) Antioxidant
E) pH stabilizer
Correct Answer: C) Lubricant
Explanation: Polysorbate 80 is a non-ionic surfactant used as a lubricant in eye drops to improve the comfort and effectiveness of the formulation.
Question 2
Hepatitis A is transmitted primarily through which of the following routes?
A) Airborne transmission
B) Bloodborne transmission
C) Orofecal transmission
D) Sexual transmission
E) Vector-borne transmission
Correct Answer: C) Orofecal transmission
Explanation: Hepatitis A is primarily transmitted through the orofecal route, often through contaminated food or water.
Question 3
Nilotinib is a targeted cancer therapy. What is its mechanism of action?
A) HER2 inhibitor
B) BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor
C) mTOR inhibitor
D) VEGF inhibitor
E) EGFR inhibitor
Correct Answer: B) BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Explanation: Nilotinib is a BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, commonly used in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
Question 4
Which of the following drugs is classified as a HER2 inhibitor and is used in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer?
A) Lapatinib
B) Nilotinib
C) Neratinib
D) Bevacizumab
E) Imatinib
Correct Answer: C) Neratinib
Explanation: Neratinib is a HER2 inhibitor used in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer, often to reduce the risk of recurrence after initial treatment.
Question 5
Alpha-lipoic acid primarily works on which of the following physiological functions?
A) Blood pressure regulation
B) Glucose metabolism
C) Fat metabolism
D) Protein synthesis
E) Electrolyte balance
Correct Answer: B) Glucose metabolism
Explanation: Alpha-lipoic acid plays a role in glucose metabolism, acting as an antioxidant and improving insulin sensitivity in some cases.
Question 6
Which of the following is the most abundant protein in the blood?
A) Fibrinogen
B) Albumin
C) Globulin
D) Hemoglobin
E) Myoglobin
Correct Answer: B) Albumin
Explanation: Albumin is the most abundant protein in the blood, playing a critical role in maintaining osmotic pressure and transporting substances.
Question 7
Which of the following classes of drugs is known to cause sexual dysfunction?
A) ACE inhibitors
B) Beta blockers
C) Calcium channel blockers
D) Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
E) Proton pump inhibitors
Correct Answer: B) Beta blockers
Explanation: Beta blockers are known to cause sexual dysfunction, including reduced libido and erectile dysfunction. Other options like ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and proton pump inhibitors are not typically associated with sexual dysfunction.
Question 8
Which of the following organisms is most commonly associated with endocarditis due to dental procedures?
A) Staphylococcus aureus
B) Streptococcus viridans
C) Enterococcus faecalis
D) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
E) Escherichia coli
Correct Answer: B) Streptococcus viridans
Explanation: Streptococcus viridans is the most common cause of bacterial endocarditis associated with dental procedures, though other organisms like Staphylococcus and Enterococcus can also cause endocarditis in different settings.
Question 9
Which of the following bacteria is also known as Group A Streptococcus?
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
B) Streptococcus pyogenes
C) Streptococcus agalactiae
D) Streptococcus viridans
E) Streptococcus mutans
Correct Answer: B) Streptococcus pyogenes
Explanation: Streptococcus pyogenes is classified as Group A Streptococcus and is responsible for various infections such as strep throat, impetigo, and rheumatic fever.
Question 10
Which of the following is the first-line treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis?
A) Topical corticosteroids
B) Methotrexate
C) Antihistamines
D) Oral antibiotics
E) NSAIDs
Correct Answer: B) Methotrexate
Explanation: Methotrexate is commonly used in moderate to severe psoriasis cases, particularly when topical treatments are insufficient. It works by suppressing the immune response.
Question 11
A patient is prescribed Nifedipine ER for hypertension. What is the most appropriate counseling point for this medication?
A) It can be crushed or broken in half for easier swallowing
B) It should be taken with food for better absorption
C) Do not break, crush, or chew the tablet
D) Take it at bedtime to reduce side effects
E) It can be taken with antacids to reduce GI upset
Correct Answer: C) Do not break, crush, or chew the tablet
Explanation: Nifedipine ER (extended release) tablets should not be broken, crushed, or chewed, as this can affect the release mechanism and lead to too much drug being absorbed at once, increasing the risk of side effects.
Question 12
Which of the following antibiotics would be ineffective against Chlamydophila pneumonia due to its resistance to cell wall synthesis inhibitors?
A) Penicillin
B) Amoxicillin
C) Doxycycline
D) Cephalexin
E) Vancomycin
Correct Answer: C) Doxycycline
Explanation: Chlamydophila pneumonia is resistant to antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis, such as penicillin, amoxicillin, and cephalexin, because it lacks a traditional peptidoglycan cell wall. Doxycycline is commonly used for treatment.
Question 13
Which of the following is the preferred first-line treatment for acute bacterial sinusitis?
A) Azithromycin
B) Amoxicillin/clavulanate
C) Ciprofloxacin
D) Clindamycin
E) Erythromycin
Correct Answer: B) Amoxicillin/clavulanate
Explanation: Amoxicillin/clavulanate is the first-line treatment for acute bacterial sinusitis due to its efficacy against common causative organisms such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
Question 14
Which of the following treatments is most appropriate for non-bullous impetigo?
A) Topical mupirocin
B) Oral doxycycline
C) Topical corticosteroids
D) Oral fluconazole
E) Topical antifungal cream
Correct Answer: A) Topical mupirocin
Explanation: Topical mupirocin is the treatment of choice for non-bullous impetigo caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It effectively eliminates the infection without the need for systemic antibiotics in mild cases.
Question 15
Which of the following statements about geometric isomerism is correct?
A) It occurs only in molecules with triple bonds
B) It occurs due to the free rotation around a single bond
C) It occurs in molecules with restricted rotation around a double bond
D) It is caused by the formation of hydrogen bonds
E) It is a form of optical isomerism
Correct Answer: C) It occurs in molecules with restricted rotation around a double bond
Explanation: Geometric isomerism occurs in molecules with restricted rotation around a double bond, leading to different spatial arrangements of substituents, such as cis and trans isomers.
Question 16
Which of the following correctly represents the formula for absolute bioavailability (F)?
A) The ratio of the area under the curve (AUC) for oral administration to the AUC for intravenous administration, adjusted for the doses.
B) The ratio of the dose administered orally to the dose administered intravenously.
C) The ratio of the maximum concentration achieved after oral administration to that after intravenous administration.
D) The difference between the AUC for oral and intravenous administration.
E) The ratio of the volume of distribution after oral administration to the volume of distribution after intravenous administration.
Correct Answer: A) The ratio of the area under the curve (AUC) for oral administration to the AUC for intravenous administration, adjusted for the doses.
Explanation: Absolute bioavailability (F) is calculated by comparing the area under the curve (AUC) of the drug after oral administration to that after intravenous administration, while adjusting for the doses administered.
Question 17
Which of the following is considered the first-line treatment for COPD management?
A) Long-acting beta agonists (LABA)
B) Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS)
C) Short-acting beta agonists (SABA)
D) Anticholinergics (LAMA)
E) Oral prednisone
Correct Answer: D) Anticholinergics (LAMA)
Explanation: Long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) are considered the first-line treatment for long-term management of COPD, as they improve lung function and reduce exacerbations.
Question 18
What is the primary mechanism of action of dexamethasone?
A) Irreversibly inhibits phospholipase A2, reducing inflammation
B) Reversibly inhibits histamine release from mast cells
C) Selectively inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines
D) Non-selectively suppresses inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis
E) Reversibly stimulates glucocorticoid receptors
Correct Answer: D) Non-selectively suppresses inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis
Explanation: Dexamethasone is a non-selective corticosteroid that inhibits prostaglandin synthesis by reducing the production of inflammatory mediators. It does not target specific inflammatory pathways selectively and works broadly to suppress inflammation.
Question 19
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of dexlansoprazole?
A) Irreversibly inhibits H+/K+ ATPase in parietal cells, reducing gastric acid secretion
B) Reversibly blocks histamine H2 receptors on parietal cells
C) Non-selectively inhibits all proton pumps in the stomach
D) Selectively binds to and inhibits proton pumps for 12 hours
E) Reversibly inhibits gastric acid secretion by blocking gastrin receptors
Correct Answer: A) Irreversibly inhibits H+/K+ ATPase in parietal cells, reducing gastric acid secretion
Explanation: Dexlansoprazole is a selective and irreversible proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that blocks the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme in parietal cells, leading to long-lasting inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
Question 20
Abiraterone is primarily used for the treatment of prostate cancer. What is its mechanism of action?
A) Irreversibly inhibits 5-alpha reductase, reducing testosterone production
B) Reversibly inhibits androgen receptor signaling
C) Irreversibly inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1, blocking androgen production
D) Selectively blocks estrogen receptors in prostate cancer cells
E) Non-selectively inhibits all steroid hormones
Correct Answer: C) Irreversibly inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1, blocking androgen production
Explanation: Abiraterone irreversibly inhibits CYP17A1, an enzyme involved in testosterone synthesis. This prevents androgen production, which is crucial for prostate cancer growth.
Question 21
Which of the following correctly describes the formula for prevalence?
A) The number of new cases of a disease divided by the total population at risk
B) The number of new and existing cases of a disease at a specific point in time divided by the total population
C) The number of people who recover from a disease divided by the total number of cases
D) The number of deaths from a disease divided by the total population at risk
E) The number of disease-free individuals divided by the total population
Correct Answer: B) The number of new and existing cases of a disease at a specific point in time divided by the total population
Explanation: Prevalence is a measure of how widespread a disease is at a specific time point and is calculated by dividing the number of new and existing cases by the total population.
Question 22
Which of the following best describes the formula for relative risk?
A) The ratio of the risk of disease in the exposed group to the risk of disease in the unexposed group
B) The difference in the number of cases between the exposed and unexposed groups
C) The ratio of the number of deaths to the number of people at risk
D) The percentage of people who survive a disease divided by the total number of cases
E) The ratio of disease-free individuals to the number of cases
Correct Answer: A) The ratio of the risk of disease in the exposed group to the risk of disease in the unexposed group
Explanation: Relative risk (RR) is a measure used in cohort studies to compare the risk of a disease between two groups: those exposed to a factor and those unexposed.
Question 23
In a clinical trial, the analysis that includes all patients originally assigned to a treatment group, regardless of whether they completed the treatment or not, is called:
A) Per-protocol analysis
B) Case-control analysis
C) Intention-to-treat analysis
D) Crossover analysis
E) Time-to-event analysis
Correct Answer: C) Intention-to-treat analysis
Explanation: Intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis includes all participants in the groups to which they were randomized, regardless of adherence to the treatment, preserving the benefits of randomization.
Question 24
Which of the following best describes Phase 2 metabolism of drugs?
A) Involves oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis reactions to make drugs more water-soluble
B) Involves conjugation reactions such as glucuronidation, sulfation, and acetylation to make drugs more water-soluble for excretion
C) Involves the filtration of drugs by the kidneys for elimination
D) Involves the binding of drugs to plasma proteins for transport
E) Involves the passage of drugs through the blood-brain barrier
Correct Answer: B) Involves conjugation reactions such as glucuronidation, sulfation, and acetylation to make drugs more water-soluble for excretion
Explanation: Phase 2 metabolism involves conjugation reactions where a drug is combined with another substance (e.g., glucuronic acid) to increase its water solubility, facilitating excretion.
Question 25
The PDSA cycle is a framework used for quality improvement in healthcare. Which of the following is the correct sequence of steps in the PDSA cycle?
A) Plan, Do, Study, Act
B) Plan, Study, Act, Do
C) Perform, Develop, Study, Assess
D) Prepare, Do, Study, Apply
E) Plan, Develop, Study, Assess
Correct Answer: A) Plan, Do, Study, Act
Explanation: The PDSA cycle stands for Plan, Do, Study, Act, which is a continuous cycle used to test changes in healthcare settings and improve quality. The process involves planning a change, implementing it, studying the results, and then acting on what has been learned to make further improvements.
Question 26
Which of the following is a delayed symptom of Lyme disease?
A) Fever and chills
B) Bull’s-eye rash
C) Joint pain and arthritis
D) Fatigue and headache
E) Localized skin infection
Correct Answer: C) Joint pain and arthritis
Explanation: A delayed symptom of Lyme disease, often occurring weeks to months after the initial infection, includes joint pain and arthritis, particularly affecting the large joints such as the knees. Early symptoms include fever, fatigue, and the bull’s-eye rash.
Question 27
A patient is diagnosed with a mild infection caused by Streptococcus and Enterococcus species. What is the first-line drug of choice for treating this infection?
A) Ciprofloxacin
B) Amoxicillin-clavulanate
C) Vancomycin
D) Penicillin + Gentamicin
E) Metronidazole
Correct Answer: B) Amoxicillin-clavulanate
Explanation: Amoxicillin-clavulanate is the drug of choice for treating mild to moderate infections caused by Streptococcus and Enterococcus species, particularly in outpatient settings. It offers broad-spectrum activity and is effective for respiratory, urinary tract, and other common infections caused by these organisms. In more severe cases (e.g., endocarditis), penicillin or ampicillin combined with gentamicin is preferred.
Question 28
Which of the following is the most common reason to switch from an ACE inhibitor to an ARB in a patient?
A) Persistent dry cough
B) Elevated blood pressure
C) Weight gain
D) Increased heart rate
E) Hyperglycemia
Correct Answer: A) Persistent dry cough
Explanation: A common side effect of ACE inhibitors is a persistent dry cough due to the accumulation of bradykinin. When this occurs, patients are often switched to an ARB (angiotensin II receptor blocker), which does not cause bradykinin accumulation and is less likely to cause a cough.
Question 29
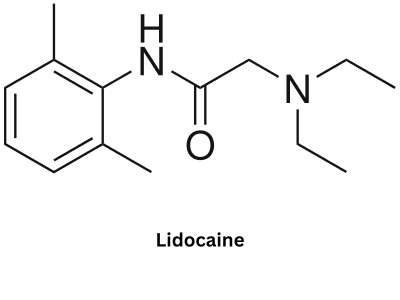
Lidocaine undergoes oxidative N-dealkylation as part of its metabolism. Which enzyme is primarily responsible for this process?
A) Monoamine oxidase (MAO)
B) Cytochrome P450 (CYP3A4)
C) Acetylcholinesterase
D) Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
E) Glutathione S-transferase (GST)
Correct Answer: B) Cytochrome P450 (CYP3A4)
Explanation: Lidocaine is metabolized in the liver by CYP3A4 and other cytochrome P450 enzymes via oxidative N-dealkylation, which removes an alkyl group from the nitrogen atom, producing metabolites such as monoethylglycinexylidide.
Question 30
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for transferring a methyl group to norepinephrine and dopamine, playing a key role in their breakdown?
A) Acetylcholinesterase
B) Monoamine oxidase (MAO)
C) Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
D) Glutathione S-transferase (GST)
E) Cytochrome P450
Correct Answer: C) Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
Explanation: Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group to catecholamines like norepinephrine and dopamine, aiding in their breakdown and regulation.
Question 31
Which of the following best describes an N-alkyl group?
A) A hydroxyl group attached to a nitrogen atom
B) An alkyl group attached to a nitrogen atom
C) An oxygen atom bonded to an alkyl chain
D) A nitrogen atom double-bonded to a carbonyl group
E) An alkyl chain attached to a sulfur atom
Correct Answer: B) An alkyl group attached to a nitrogen atom
Explanation: An N-alkyl group is an alkyl chain attached to a nitrogen atom. It is commonly found in organic compounds such as amines, where the nitrogen atom is bonded to one or more alkyl groups.
Question 32
Which of the following describes the mechanism of action of nitric oxide in the body?
A) Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, reducing inflammation
B) Stimulates guanylate cyclase, increasing cGMP and causing vasodilation
C) Binds to beta-adrenergic receptors, causing bronchodilation
D) Blocks calcium channels, reducing smooth muscle contraction
E) Inhibits acetylcholinesterase, increasing acetylcholine levels
Correct Answer: B) Stimulates guanylate cyclase, increasing cGMP and causing vasodilation
Explanation: Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase, which increases cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels. This leads to smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation, playing a critical role in regulating blood pressure and blood flow.
Question 33
What is the mechanism of action of zoledronate in the treatment of osteoporosis?
A) Increases calcium absorption from the intestines
B) Inhibits bone resorption by blocking osteoclast activity
C) Stimulates osteoblasts to produce more bone
D) Inhibits vitamin D synthesis
E) Increases parathyroid hormone secretion
Correct Answer: B) Inhibits bone resorption by blocking osteoclast activity
Explanation: Zoledronate, a bisphosphonate, works by inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption, helping to increase bone density and reduce the risk of fractures in conditions such as osteoporosis.
Question 34
Which of the following best describes Grave’s disease?
A) An autoimmune disorder characterized by the destruction of the thyroid gland
B) A viral infection of the thyroid that causes transient hyperthyroidism
C) An autoimmune disorder where the body produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to hyperthyroidism
D) A bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland
E) A deficiency in thyroid hormone production due to iodine deficiency
Correct Answer: C) An autoimmune disorder where the body produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to hyperthyroidism
Explanation: Grave’s disease is an autoimmune disorder where the body produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) that mimic thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), causing the thyroid to produce excessive thyroid hormones and leading to hyperthyroidism.
Question 35
Which of the following is a common side effect of SGLT2 inhibitors?
A) Hypertension
B) Urinary tract infections
C) Weight gain
D) Bradycardia
E) Constipation
Correct Answer: B) Urinary tract infections
Explanation: SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g., empagliflozin, canagliflozin) commonly cause urinary tract infections and genital infections due to increased glucose in the urine, which promotes bacterial and fungal growth.
Question 36
What is the mechanism of action of febuxostat in the treatment of gout?
A) Inhibits xanthine oxidase, reducing uric acid production
B) Increases the excretion of uric acid through the kidneys
C) Binds to uric acid crystals, dissolving them
D) Blocks uric acid reabsorption in the proximal tubules
E) Reduces inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis
Correct Answer: A) Inhibits xanthine oxidase, reducing uric acid production
Explanation: Febuxostat is a selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor, which blocks the conversion of hypoxanthine to uric acid, thereby reducing uric acid levels in patients with gout.
Question 37
Which of the following is a common side effect of allopurinol?
A) Hepatotoxicity
B) Bone marrow suppression
C) Skin rash
D) Peripheral neuropathy
E) Nephrotoxicity
Correct Answer: C) Skin rash
Explanation: Allopurinol can cause skin rash, which can range from mild to severe. In rare cases, it may lead to more serious reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Question 38
What is the mechanism of action of trazodone?
A) Selectively inhibits serotonin reuptake
B) Antagonizes serotonin receptors and weakly inhibits serotonin reuptake
C) Inhibits dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake
D) Blocks acetylcholine receptors
E) Stimulates GABA receptors
Correct Answer: B) Antagonizes serotonin receptors and weakly inhibits serotonin reuptake
Explanation: Trazodone works by antagonizing serotonin 5-HT2A receptors and weakly inhibiting serotonin reuptake, which helps with depression and insomnia.
Question 39
What is the mechanism of action of mirtazapine?
A) Selectively inhibits serotonin reuptake
B) Antagonizes alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, enhancing the release of norepinephrine and serotonin
C) Inhibits dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake
D) Blocks serotonin receptors and enhances GABA activity
E) Inhibits monoamine oxidase
Correct Answer: B) Antagonizes alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, enhancing the release of norepinephrine and serotonin
Explanation: Mirtazapine is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor antagonist, which increases the release of norepinephrine and serotonin, contributing to its antidepressant effects.
Question 40
Which of the following best describes incidence in epidemiology?
A) The total number of cases of a disease at a given time
B) The number of new cases of a disease over a specified period, divided by the population at risk
C) The number of deaths from a disease in a specific period
D) The ratio of disease-free individuals to the total population
E) The likelihood of recovering from a disease
Correct Answer: B) The number of new cases of a disease over a specified period, divided by the population at risk
Explanation: Incidence refers to the number of new cases of a disease that occur during a specific time period, divided by the population at risk of developing the disease.
Question 41
Which of the following is a risk factor for osteoporosis?
A) Increased physical activity
B) High body mass index (BMI)
C) Smoking
D) High estrogen levels
E) Low sodium intake
Correct Answer: C) Smoking
Explanation: Smoking is a well-known risk factor for osteoporosis as it reduces bone density by affecting bone turnover. Other risk factors include menopause, low calcium intake, sedentary lifestyle, and chronic corticosteroid use.
Question 42
Which of the following is an appropriate first-line treatment for head lice in a patient without allergies?
A) Ivermectin
B) Malathion lotion
C) Permethrin 1% lotion
D) Lindane shampoo
E) Oral metronidazole
Correct Answer: C) Permethrin 1% lotion
Explanation: Permethrin 1% lotion is a first-line treatment for head lice. It is an over-the-counter topical pediculicide that works by disrupting sodium channels in the lice’s nerve cells, leading to paralysis and death of the lice. It is safe and effective for most patients.
Question 43
Which of the following is the most common causative organism of bacterial meningitis in adults?
A) Escherichia coli
B) Neisseria meningitidis
C) Streptococcus pneumoniae
D) Listeria monocytogenes
E) Haemophilus influenzae
Correct Answer: C) Streptococcus pneumoniae
Explanation: Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in adults. It can cause severe, life-threatening infections, and prompt treatment with appropriate antibiotics is essential.
In the context of bacterial meningitis in neonates, Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae are not the most common pathogens. Here’s an overview of their relevance:
- Neisseria meningitidis is a significant cause of bacterial meningitis in older children, adolescents, and adults but is not a common cause in neonates. In neonates, bacterial meningitis is more commonly caused by Group B Streptococcus (GBS), Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes.
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae is associated with neonatal conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum), but it does not commonly cause bacterial meningitis in neonates. It can lead to other infections in newborns, such as sepsis, but is rarely a cause of neonatal meningitis.
Question 44
A 28-year-old woman presents with itching, burning, and an abnormal vaginal discharge. Which of the following is the most likely cause of vaginitis if the discharge is thick, white, and odorless?
A) Bacterial vaginosis
B) Trichomoniasis
C) Candidiasis
D) Gonorrhea
E) Chlamydia
Correct Answer: C) Candidiasis
Explanation: Candidiasis, or a yeast infection, is the most likely cause of vaginitis when the discharge is thick, white, and odorless (often described as cottage cheese-like). It is caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans in the vagina.
Question 45
Which of the following is considered the most potent corticosteroid used in dermatology for severe inflammatory skin conditions?
A) Hydrocortisone 1%
B) Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
C) Clobetasol propionate 0.05%
D) Triamcinolone acetonide 0.1%
E) Fluocinolone acetonide 0.01%
Correct Answer: C) Clobetasol propionate 0.05%
Explanation: Clobetasol propionate 0.05% is a super-high potency corticosteroid, used for severe inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and other resistant dermatoses. It should be used for short durations due to the risk of side effects such as skin atrophy.
Question 46
A child presents with signs of dehydration, and lab results indicate low MCU (mean corpuscular volume). What is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Iron deficiency anemia
B) Folate deficiency
C) Vitamin B12 deficiency
D) Hemolytic anemia
E) Thalassemia
Correct Answer: A) Iron deficiency anemia
Explanation: Low MCU (mean corpuscular volume) indicates that red blood cells are smaller than normal, which is characteristic of iron deficiency anemia. This is the most common cause of low MCU, especially in children with poor dietary iron intake or increased needs.
Question 47
A 30-year-old woman presents with vaginal discharge. A vaginal pH test reveals a pH of 6.5. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her vaginitis?
A) Candida albicans
B) Trichomonas vaginalis
C) Group B Streptococcus
D) Bacterial vaginosis
E) Lactobacillus overgrowth
Correct Answer: B) Trichomonas vaginalis
Explanation: A vaginal pH of 6.5 is suggestive of trichomoniasis (caused by Trichomonas vaginalis), which tends to occur at a higher pH (> 6.5). In contrast, bacterial vaginosis typically presents with a pH of around 4.5 or slightly higher, and Candida infections usually occur with a normal pH (around 4.0–4.5).
Question 48
Which of the following is the most appropriate first-line treatment for a patient with new-onset atrial fibrillation who is hemodynamically stable?
A) Immediate electrical cardioversion
B) Oral anticoagulation (e.g., apixaban) and rate control with a beta-blocker (e.g., metoprolol)
C) Thrombolytic therapy (e.g., alteplase)
D) Coronary stenting with clopidogrel
E) Amiodarone as monotherapy
Correct Answer: B) Oral anticoagulation (e.g., apixaban) and rate control with a beta-blocker (e.g., metoprolol)
Explanation: For new-onset atrial fibrillation in a hemodynamically stable patient, oral anticoagulation (such as apixaban or warfarin) is used to reduce stroke risk, and rate control with a beta-blocker (e.g., metoprolol) or a calcium channel blocker (e.g., diltiazem) is used to control heart rate. Rhythm control may be considered later if necessary.
Question 49
Which of the following best differentiates NSTEMI from STEMI in terms of their presentation on an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
A) NSTEMI presents with ST-segment elevation, while STEMI does not
B) NSTEMI presents with ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion, while STEMI shows ST-segment elevation
C) Both NSTEMI and STEMI present with normal ECG findings
D) NSTEMI and STEMI both present with ST-segment elevation but NSTEMI shows no troponin elevation
E) STEMI has no troponin elevation while NSTEMI does
Correct Answer: B) NSTEMI presents with ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion, while STEMI shows ST-segment elevation
Explanation: NSTEMI (Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction) typically presents with ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion on ECG, while STEMI (ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) is characterized by ST-segment elevation. Both conditions involve troponin elevation, indicating myocardial damage.
Question 50
Which of the following is the initial treatment strategy for a patient with NSTEMI?
A) Thrombolytic therapy
B) Immediate percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
C) Antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, and beta-blockers
D) Immediate coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
E) Nitroglycerin and aspirin only
Correct Answer: C) Antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, and beta-blockers
Explanation: The initial treatment for NSTEMI includes antiplatelet therapy (aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitors), anticoagulation (heparin), beta-blockers, and nitrates. Unlike STEMI, thrombolytic therapy is not recommended for NSTEMI unless the patient progresses to STEMI.
Important structures for exam